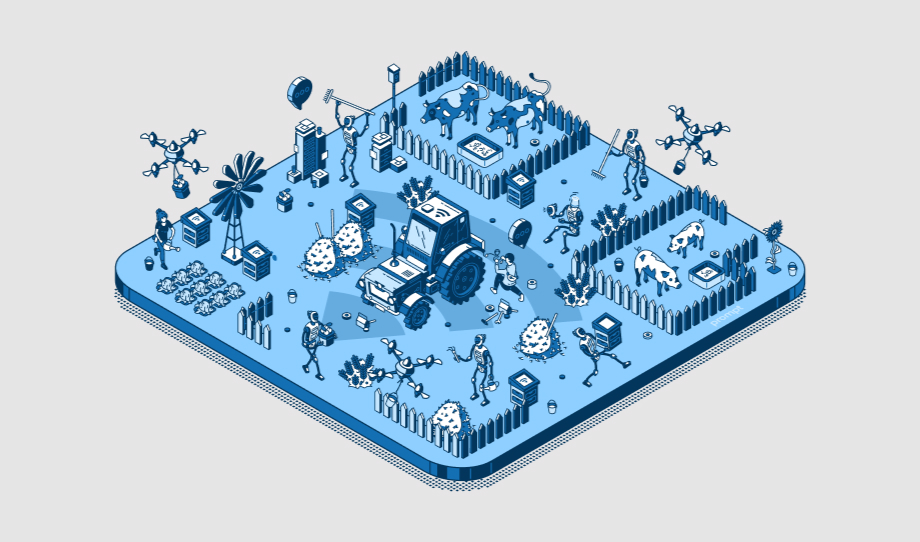
How will Smart Farming decide the Future of Agriculture?
Today, farmers are facing more pressure than ever before. Demand for food is growing as the…
How IoT Boosts the Micro Mobility Market?
The Internet of Things is no new thing in the tech market. Just look around, and…
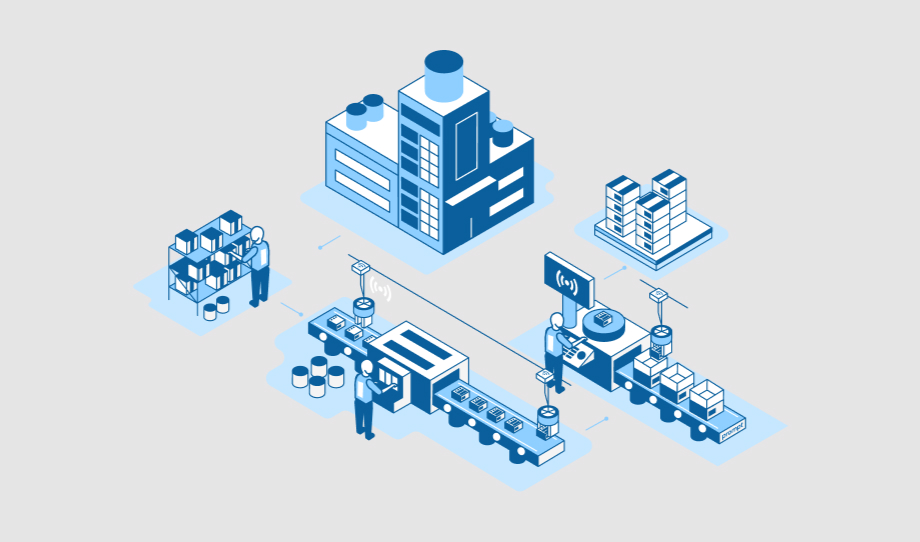
How can IoT Sensors Improve Productivity in Manufacturing?
Internet of Things has been reaching out to almost every sector, and as a result, it…