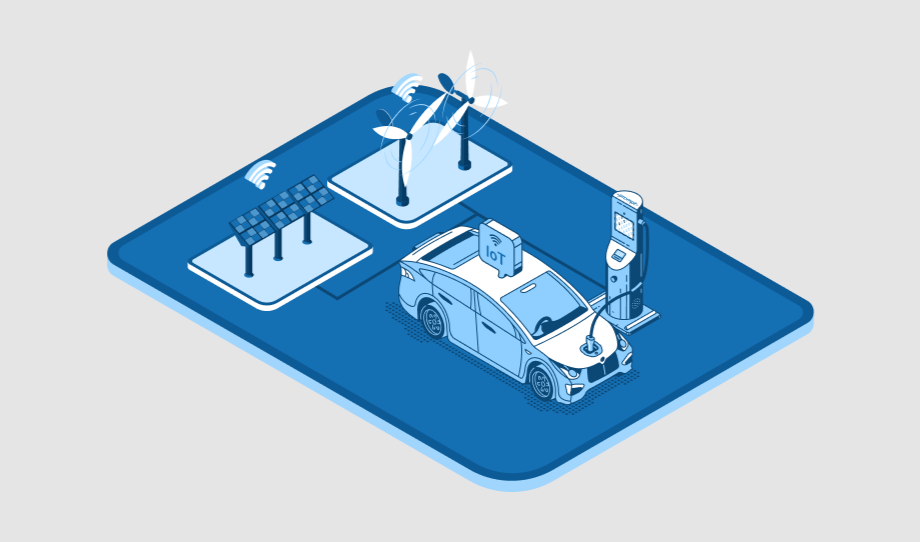
How IoT supports Electric Vehicle Charging and Keeps EVs Running
The evolution in the vehicle industry is remarkable. The increasing vehicle demand is not just consuming…
What are Skills and Apps Needed for IoT Mobile App Development?
Nowadays, it is quite apparent that most of the Internet of Things that is IoT solutions…